Brain Stroke Treatment
Stroke is a condition which occurs when a part of the human brain is deprived of blood (thrombosis or embolism) or a blood vessel bursts and blood puts pressure on the brain.
Stroke Unit
The department of Neurology at Shalby is backed by Neurosurgery and Neuro-radiology. Together these three departments deliver the most aggressive treatment in cases of a Stroke.
Alarming Facts about Stroke:
- World over, One in Six people will have a stroke in their lifetime
- Stroke kills someone every six seconds
- Every other second stroke attacks a person, regardless of age or gender
- Fifteen million people experience a stroke every year and six million of them do not survive
- Stroke is a third leading cause of death in India
- The incidence of stroke is 130 per 100,000 populations every year
- About 20% of heart patients are susceptible to stroke
Be Stroke Smart
- Reduce the risk
- Recognize symptoms
- Respond FAST - call 108
Most Important
The earlier the treatment, the better the outcome with minimum lasting damage to body functions.
Risk Factors
Risk factors which may lead to stroke are:
- Old age
- Family history
- Men are more likely to have a stroke
- More stroke deaths occur in women
Modifiable Risks:
- Smoking habit
- Lack of exercise
- Excessive Alcohol
- Obesity
Other Risk Factors:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes Mellitus
Controlling risk factors reduces possibility of stroke. So if you have any of the above conditions please eat and exercise regularly and get health check-ups regularly.
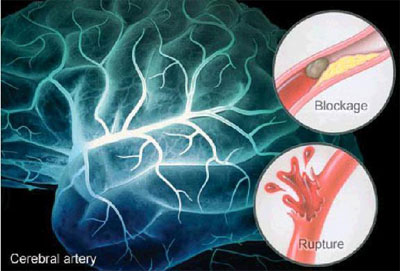
Causes
- Atherosclerosis – hardening of the arteries and formation of clot
- Plaque build-up in the arteries, leaving less space for blood to flow
- Blood clot lodged in the narrow space of blood vessels causing an ‘ischemic stroke’
- Hemorrhagic strokes – high BP that causes a weak artery to burst
Symptoms
Stroke symptoms appear suddenly and they must always be treated as a medical emergency. They include a sudden onset of any of the following symptoms:
- Weakness of the face, arm, and/or leg on one side of body
- Numbness in the face, arm, and/or leg on one side of body
- Inability to understand spoken language
- Inability to speak
- Inability to write
- Vertigo and/ or gait imbalance
- Double vision
In Hospital
When a stroke victim arrives in Shalby, after a clinical exam, the 128 slice CT scan of the brain (done in seconds) reveals hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke. If Stroke is hemorrhagic one, treatment is surgical and/ or conservative. If stroke is ischemic, treatment depends upon the time lag. The earlier a stroke patient is brought to Shalby, the better are chances of their recovery. The first 4.5 hours are critical for treatment.
Types of Stroke
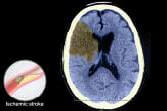
Ischemic Stroke:
The most common type of stroke is known as an ischemic stroke. Nearly nine out of 10 strokes fall into this category. The culprit is a blood clot that obstructs a blood vessel inside the brain. The clot may develop on the spot or travel through the blood from other parts of the body like the heart.
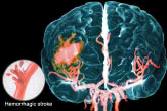
Hemorrhagic Stroke:
Hemorrhagic strokes are less common but are more likely to be fatal. They occur when a weakened blood vessel in the brain bursts. The result is bleeding inside the brain that can be difficult to stop.
TIA:
Means ‘Transient Ischemic Attack’ and is often called a ‘minor-stroke’. It needs Immediate Action. So TIA is often called ‘Take Immediate Action’. Blood flow is temporarily impaired to part of the brain, causing symptoms similar to an actual stroke. When the blood flows again, the symptoms disappear.
A TIA is a warning sign that a stroke may happen soon. It’s critical to see your doctor if you think you’ve had a TIA. Therapies help reduce stroke risk.
More Time Lost = More Damage
Every second counts when seeking treatment for a stroke. When deprived of oxygen, brain cells begin dying within minutes. Administering clot dissolving drugs can curb brain damage, if given in 4.5 hours of symptoms. Once brain tissue has died, the body parts controlled by that area will not work properly.
Testing Severity by F.A.S.T. method:
It is a simple test to check severity and level of Stroke.
Face: Check smile. One side droops?
Arms: When raised, does one side drift down or fall down?
Speech: Can the person repeat a simple sentence? Do words slur?
Time: Time is critical. Call 108 immediately if any symptoms are present.
Diagnosis of Stroke
Transcranial Doppler:
- Noninvasive method
- Bedside procedure
- Brain blood vessels are visualized in real time
- Used for diagnosis as well as treatment of Stroke
- Used for monitoring small blood clots in brain
128 Slice CT Scan
- Very fast Angiography & CT Scan in fraction of a second
- Done without sedation
- Sections as thin as 0.6 mm can be visualized
- Images are sharp and clear
- 3D reconstruction of all parts of brain can be seen
- Perfusion studies show how much blood supply the brain is receiving
- Virtual studies are possible
Management of Stroke
Follow these steps while rushing the patient to hospital:
- Keep the patient in the lateral position
- Do not elevate the head
- Keep the past history of the patient with details of diseases and medicines ready
Golden Period
The first 4.5 hours are called the golden time for treating stroke because ideal treatment if given in this period leads to better outcomes.
During transit
The attending doctor or paramedic will check the following:
- Circulation & BP is monitored
- Breathing is monitored
- Airways are kept open
- IV line is secured
In the Hospital Care
- Two IV lines secured
- Immediate CT scan of brain (128 slices)
- Regulate BP
- Ventilator support
- Blood investigations
- ECG
- Echocardiography
- Carotid and Trans-Cranial Doppler
Technology
- 128 slice CT Scan
- Transcranial Doppler
- Digital Subtraction Angiography of Brain
- Dedicated Stroke Team
Emergency Care
For an ischemic stroke, emergency treatment focuses on medicine to restore blood flow. A clot-busting medication is highly effective at dissolving clots and minimizing long-term damage, but it must be given within 4.5 hours of the onset of symptoms. Hemorrhagic strokes are treated by controlling high BP, bleeding, and the swelling in the brain through surgery if needed.
Prevention
These steps help in preventing of stroke:
Stent
If the carotid artery (which supplies blood to the brain) is clogged, and the patient has symptoms of TIA or stroke, a procedure called carotid angioplasty with a stent is done. This restores blood supply to the brain.
Endarterectomy
Blocked Carotid arteries may be opened by surgical removal of plaques formed due to atherosclerosis to restore the blood flow.
Thrombolysis
Thrombolysis is a type of treatment given in stroke where clots in blood vessels are dissolved by medicines. Use of ultrasound enhances the effect of thrombolysis. Hence thrombolysis is combined with TCD Ultrasonography to get better results in cases of stroke.
Depending on how quickly the patient has been brought to the hospital, Stroke will be treated as follows:
- Intra-venous treatment is given when patient is brought within 4.5 hours
- Intra-arterial treatment is given when patient is brought within 9 hours
Book Your Appointment to get the best brain stroke treatment in India
Blog/Tips of the day

Signs That You’re Having a Migraine
A migraine and Headache, both are such irritating, throbbing pains that can make you completely uncomfortable and spoil your mood as well as your entire day. Due to their almost similar nature and intensity, many times it becomes difficult to differentiate between them. A majority of people fail to identify... Read MoreShalby Hospital
Neuro Science
Center Of Excellence
- Arthroscopy – Sports Injury
- Ophthalmology and Glaucoma
- Oncosurgery
- Oncology
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Obesity Surgery
- Neuro Science
- Neurosurgery
- Nephrology
- Orthopedic and Trauma
- Paediatric Orthopedics
- Spine Surgery
- Rheumatology
- Radiology and Imaging
- Pulmonology and Chest
- Plastic Surgery
- Paediatrics and Neonatology
- Pathology And Microbiology
- Maxillofacial Surgery
- Knee Joint Replacement
- ENT Surgery
- Endoscopy and Laparoscopy
- Endocrinology – Diabetology
- Emergency Medicine
- Dental Cosmetic and Implantology
- Cosmetic and Aesthetic
- Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery
- Cardiology
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- Gastroenterology
- Intensive and Critical Care
- Infertility and IVF
- Infectious Diseases
- Hip Joint Replacement
- Liver Transplant
- Hair Transplant
- General Surgery
- General Medicine
- Uro Surgery
- Dermatology
- Arthroplasty
- Psychiatry
- Urology
- Anesthesia












