Rheumatology - Arthritis Treatment
What is Rheumatology?
Rheumatology is a special branch of medicine which deals with the treatment programs for arthritis and various forms of Collagen Vascular Diseases. Arthritis is a common disease condition observed in India but very few hospitals in the country provide specialized care to patients suffering from Arthritis. Arthritis deformities can be prevented and disease-remission can be achieved thorough arthritis care at Shalby Hospitals, India.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Symptoms
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) affects not only your joints but also a wide variety of internal organs. The symptoms vary in severity with periods of flares where pain shoots up and relative remissions where symptoms fade. RA affects your joint linings, which result in bone erosion and joint deformity.
Early symptoms of RA include:
- Tender and swollen joints
- Stiffness in joints, usually after periods of inactivity
- Fatigue
- Fever and loss of appetite
In the early stages, symptoms of RA can be seen in joints of fingers and toes. As it progresses, symptoms spread to other joints like knees, elbows, hips and shoulders. In 40 per cent of cases, RA can affect skin, eyes, kidneys, heart, nerve tissue, salivary glands and many non-joint organs.
Symptoms range from mild to severe. So, it is advisable not to ignore them and consult a physician.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
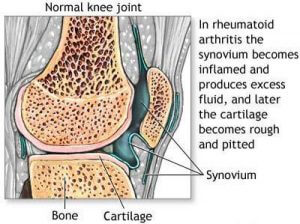
Rheumatoid Arthritis is an autoimmune disease, which means that your immune system attacks your body tissues. It occurs when your immune system attacks the synovium, a soft tissue that covers the inner surface of a joint and inflames the joint/s.
This inflammation increases the thickness of synovium. The ligaments that hold the joint in place weaken and eventually stretch. This causes the joint to lose shape and its alignment. In the long term, this condition destroys the cartilage and also corrodes the bone within the joint.
It is not yet concrete as to what kicks off your immune system. It is believed that genes play an important role in this process. It doesn’t mean that your genes cause RA; you are more susceptible to the onset due to infection from certain bacteria and viruses.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Risk Factors
Although there is a consensus that there is a genetic component involved in the onset of the disease, there are many environmental factors that may increase the risk of RA:
-
- Age: People of any age can get affected by Rheumatoid Arthritis. But those in middle age are more susceptible to get the disease.
-
- Gender: Statistically, men are less likely to develop Rheumatoid Arthritis than women. Women are also less likely than men to achieve remission.
-
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking increases your risk of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis. The risk is higher if your genetic makeup has a higher risk of developing RA.
- Obesity: Obesity is also linked as a risk factor for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Women of age 55 or younger who are obese are mainly in the high-risk category.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
Rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis requires a series of lab tests and clinical examinations. Your physician performs a physical exam of your joints. The examinations include:
- Examining for swelling or redness around joints
- Joint mobility
- Checking for tenderness and warmth of the joints
- Reflexes and strength of muscles
Additionally, you may also need to get an Ultrasound, X-ray or MRI to image your joints. To determine whether you have RA, your blood is also tested. These tests are:
-
- Rheumatoid Factor Test: This test is done to check for a protein called rheumatoid factor. High Rh factor is associated with RA.
-
- Anticitrullinated Protein Antibody Test: Also called the anti-CCP test, this checks for antibodies associated with RA. This is more specific than the RF test.
-
- Antinuclear Antibody Test: This test is to check whether your body is producing antibodies.
-
- Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate: This test helps to determine the degree of inflammation in your body.
- C – reactive protein Test: Your liver produces C-reactive protein to tackle inflammation. High levels of this marker are associated with RA.
Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Presently, there is no cure for Rheumatoid Arthritis, though there are treatments available to help manage the symptoms and lead a better life. If treatment is started early, it’s possible to achieve remission of symptoms. One of the best ways forward for patients and physicians alike is to slow the progression of the disease.
The treat-to-target approach has proved effective in reducing symptoms and achieving higher remission rates in patients. The treatment method is:
-
- Setting specific testing goals that signal remission
- Monthly monitoring and constant assessment of the progress and management plan
- Trying alternate medications if there is no observable progress
To decrease inflammation in the joints, treatments are:
- Medications like corticosteroids, acetaminophen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Home remedies like assistive devices, applying heat or cold
- Dietary changes like switching to foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, Vitamins A, C and E
- Specific exercises as prescribed by the doctor
Types of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Many-a-times, Rheumatoid Arthritis is confused with Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis is not an autoimmune disease. It often sets in the middle to old age due to regular wear and tear of the joints.
There are three types of Rheumatoid Arthritis depending on the protein called Rheumatoid factor –
-
- Seropositive RA: If your blood tests positive for Rheumatoid factor in either Rheumatoid factor test or the Anti-CCP test, you might have Seropositive RA. This means that your body is reacting to your healthy tissues. It releases antibodies that attack your cells. More than 80 per cent of people who have RA are seropositive or RF positive.
-
- Seronegative RA: Even if your blood tests negative for this protein, you can still suffer from RA. In seronegative RA patients, the joints will still be swollen and they will have difficulty in joint mobility. People who are RF negative often tend to have milder symptoms of RA as compared to RF positive ones.
- Juvenile RA: Juvenile RA is most common in children below the age of 17. Symptoms of Juvenile RA are inflammation, stiffness and pains in joints. In severe cases, the disease can cause inflammation of the eye and can interfere in the growth and development of the patient.
Best Rheumatologist in India
With many specialty hospitals in India, there are a lot of talented and experienced Rheumatologists around the country. Shalby multi-specialty Hospital chain is prominent among them.
Shalby Rheumatology Clinic offers the following facilities
At Shalby Hospitals, we have established the permanent Rheumatology OPD wherein Rheumatologist evaluates the patients suffering from arthritis. Updated investigative back up facilities in the form of imaging and laboratory test, are also provided to the patients. The specialized orthopaedician treats all patients with treatments like arthroscopy, joint replacement, and other associated corrective surgeries.
- Consultative and continuous patient care
- Arthrocentesis
- Intra-articular injections
- Rheumatologic procedures
- Crystal identification with polarizing microscopy
- Physiotherapy
- Lab & imaging backup

Diagnosis and Management of the following diseases is available at Shalby Hospitals:
The Rheumatology unit is dedicated to provide comprehensive care to patients suffering from below conditions…
- Musculoskeletal and joint disorders: Back pain, Cervical Spondylosis, etc.
- Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteoarthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, etc.
- Osteoporosis and other metabolic bone diseases
- Chronic pain syndromes
- PUO
“Systemic autoimmune & connective tissue diseases: Lupus-SLE, Myositis, Sjogrens Syndrome, Vasculitis, Scleroderma, Sarcoidosis, etc.”
Immune mediated haemotologic diseases: ITP, Autoimmune Haemolytic Anaemia, etc.
Visit Shalby Hospital’s for Rheumatology Treatment Clinic for arthritis treatment, Gout, Septic Arthritis, Golfer’s Elbow, Osteoarthritis, and Lupus treatments by India’s best rheumatologist.
OUR Branches Available in Many Cities of India Like | Surat | Jabalpur | Indore | Jaipur
Get all information about our branches Click Here
Shalby Hospital
Rheumatology
Center Of Excellence
- Arthroscopy – Sports Injury
- Ophthalmology and Glaucoma
- Oncosurgery
- Oncology
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Obesity Surgery
- Neuro Science
- Neurosurgery
- Nephrology
- Orthopedic and Trauma
- Paediatric Orthopedics
- Spine Surgery
- Rheumatology
- Radiology and Imaging
- Pulmonology and Chest
- Plastic Surgery
- Paediatrics and Neonatology
- Pathology And Microbiology
- Maxillofacial Surgery
- Knee Joint Replacement
- ENT Surgery
- Endoscopy and Laparoscopy
- Endocrinology – Diabetology
- Emergency Medicine
- Dental Cosmetic and Implantology
- Cosmetic and Aesthetic
- Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery
- Cardiology
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- Gastroenterology
- Intensive and Critical Care
- Infertility and IVF
- Infectious Diseases
- Hip Joint Replacement
- Liver Transplant
- Hair Transplant
- General Surgery
- General Medicine
- Uro Surgery
- Dermatology
- Arthroplasty
- Psychiatry
- Urology
- Anesthesia












