Angioplasty and Stenting
Angioplasty Surgery (Also known as: Balloon Angioplasty)
Angioplasty Surgery is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. i.e. coronary arteries.
A stent used for expanding the coronary artery from inside, is a small, metal mesh tube, which is often placed after angioplasty. It helps to prevent the artery from closing up again. A Drug Eluting stent has medicine on it that helps prevent reblocking inside the stent. Rely on your cardiologist to decide which one is best suited for you. .
Description
A patient will be administered some pain medicine before an angioplasty procedure begins. To prevent blood clot, you may also be given blood thinning medicines. The doctor will make a small incision on your body, mostly near the groin, by placing you in a lie down position on a padded table.
Then your doctor will insert a catheter (flexible tube) through the incision into an artery. You will be awake during the procedure.Using live- X-ray pictures the doctor will carefully guide the catheter up into your heart and arteries. A Dye will be injected into your body to highlight blood flow through the arteries. Then a guide wire is moved into and across the blockage and a balloon catheter is pushed over the guide and into the blockage. This helps the doctors to see any blockages in the blood vessels that lead to your heart.
Followed by this procedure, a stent (wire mesh tube) would be placed in the blocked area. The stent is inserted along with the balloon catheter and the balloon is subsequently inflated. The stent is then placed which helps the artery to remain open.
Certain cancers in the female genital tract can be prevented with vaccination.
Some individuals will experience simple starting spells, while others may have violent shaking and loss of alertness. A type of endoscope known as arthroscope is used in performing this procedure.
To get the best angioplasty surgery for heart disease treatment at a reasonable cost by India's top surgeonsBook your appointment online with the best Shalby Hospitals doctors.
Why the procedure is performed?
Arteries can become narrowed or blocked by deposits called plaque. Plaque is made up of fat and cholesterol that builds up on the inside of the artery walls. This condition is called atherosclerosis.
Not every blockage can be treated with angioplasty. Some need coronary bypass (heart surgery).
Angioplasty may be used to treat:
- Persistent chest pain (angina) that medicines cannot control
- Blockage of one or more coronary arteries that puts you at risk of a heart attack
- Blockage in a coronary artery during or after a heart attack
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to your legs. These peripheral arteries can become blocked with fatty material that builds up inside them. This is called atherosclerosis.
A stent is a small, metal mesh tube that expands inside an artery.
Angioplasty & Stenting – Peripheral Arteries
Angioplasty and stent placement are two ways to open blocked peripheral arteries.
Description
In angioplasty, your blocked artery is widened with a medical “balloon.” The balloon presses against the inside wall of your artery to open your artery and improve blood flow.
Angioplasty can be done in these arteries to treat a blockage in your leg:
- Aorta – the main artery that comes from your heart
- Iliac artery – in your hip
- Femoral artery – in your thigh
- Popliteal artery – behind your knee
- Tibial and peroneal artery – in your lower leg
Before the procedure, you will be given medicine to help you relax. You will be awake but sleepy. You may also be given blood-thinning medicine to stop a blood clot from forming.
You will lie down on your back on a padded operating table. Your surgeon will inject some numbing medicine into the area that will be treated, so that you do not feel pain. This is called local anesthesia. Your surgeon will then make a small incision (cut) in your skin, usually near your groin. Your surgeon will insert a catheter (a flexible tube) through the incision into the blocked artery.
Your surgeon will be able to see your artery with live x-ray pictures. This kind of x-ray is called fluoroscopy. Dye will be injected into your body to show blood flow through your arteries. The dye will make it easier to see the blocked area. Your surgeon will carefully guide the catheter through your artery to the area where it is blocked.
Next your surgeon will pass a guide wire through the catheter to the blockage. The surgeon will push another catheter with a very small balloon on the end over the guide wire and into the blockage. The balloon is then blown up. This opens the blocked vessel and restores proper blood flow.
A stent may also be placed in the blocked area. The stent is inserted at the same time as the balloon catheter. It expands when the balloon is blown up. The stent is left in place to help keep the artery open. The balloon is then removed.
Why the procedure is performed?
Symptoms of a blocked peripheral artery are pain, achiness, or heaviness in your leg that starts or gets worse when you walk.
Reasons for having this surgery are:
- When your symptoms keep you from doing daily tasks, and they do not get better with other medical treatment.
- Skin ulcers or wounds on the leg that do not get better
- Infection or gangrene on the leg
- Pain in your leg (caused by narrowed arteries) that happens even when you are resting (called rest pain of critical limb ischemia)
Book Your Appointment for Angioplasty Surgery, Balloon Angioplasty, Retrograde Angioplasty, Angioplasty & Stent Placement in India.
Blog/Tips of the day
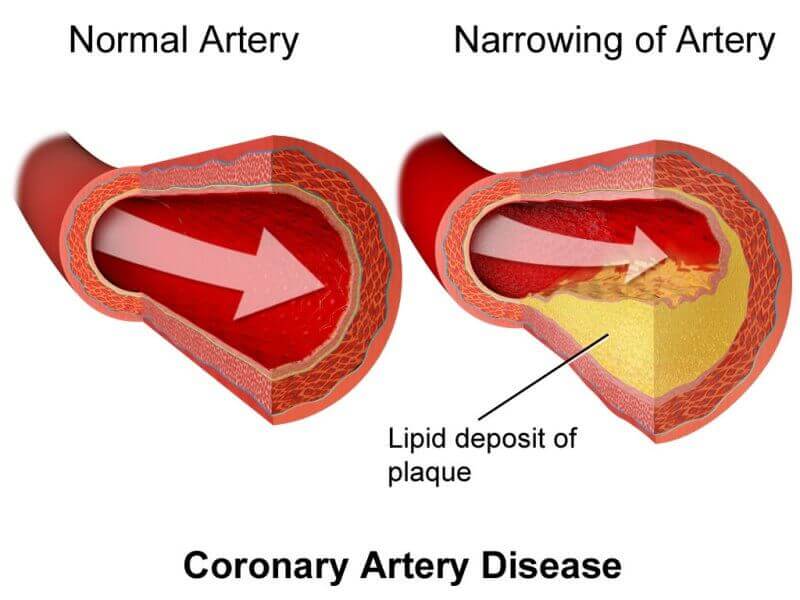
Coronary Angioplasty: A Life Saving Procedure
Angioplasty is the process mostly recommended to treat coronary artery disease - a condition that arises when plaque deposit on the inner walls of the arteries make them narrow and rigid. This apparently inhibits the blood flow to the heart muscle which then becomes deficient in oxygen. The plaque can... Read MoreShalby Hospital
Cardiology
Center Of Excellence
- Arthroscopy – Sports Injury
- Ophthalmology and Glaucoma
- Oncosurgery
- Oncology
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Obesity Surgery
- Neuro Science
- Neurosurgery
- Nephrology
- Orthopedic and Trauma
- Paediatric Orthopedics
- Spine Surgery
- Rheumatology
- Radiology and Imaging
- Pulmonology and Chest
- Plastic Surgery
- Paediatrics and Neonatology
- Pathology And Microbiology
- Maxillofacial Surgery
- Knee Joint Replacement
- ENT Surgery
- Endoscopy and Laparoscopy
- Endocrinology – Diabetology
- Emergency Medicine
- Dental Cosmetic and Implantology
- Cosmetic and Aesthetic
- Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery
- Cardiology
- Gastrointestinal Surgery
- Gastroenterology
- Intensive and Critical Care
- Infertility and IVF
- Infectious Diseases
- Hip Joint Replacement
- Liver Transplant
- Hair Transplant
- General Surgery
- General Medicine
- Uro Surgery
- Dermatology
- Arthroplasty
- Psychiatry
- Urology
- Anesthesia












