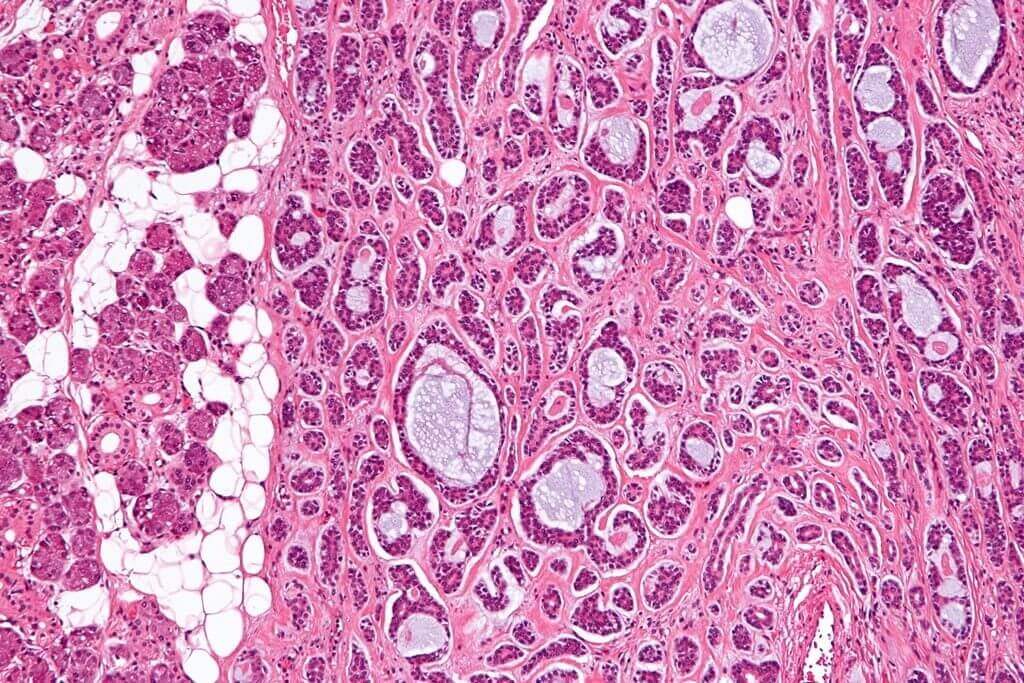
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC) is a cancer type which usually starts from the salivary glands. These glands are present on both the sides of your jaw below the jawbone and under the tongue. It may occur at other place as well in the body; like skin, bones, lacrimal gland, trachea, lungs, liver, breast, cervix and prostate. It can also occur in other sites like your mouth and throat or in other areas of the body like sweat and tear glands. This can happen anytime between your teen years till an elderly age of 80.
We have three pairs of major salivary glands under and behind your jaw; parotid, sublingual and submandibular. Many other tiny salivary glands are located inside your cheeks, and throughout your throat and mouth.
ACC grows slowly but relentlessly. It tends to be invasive at local points and infiltrates the covering of the surrounding nerve fibres (perineural spaces). There are more chances of ACC recurring; years later at the site where the tumor first arose. There are high chances of ACC metastasising to distant sites rather than just the neighbouring lymph nodes. Lung is the most common site of metastasis followed by liver. Bone metastasis indicates poor prospects for the patient.
Like other cancers, the cause of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma is also not known, but experts link it to some carcinogens like pollution or asbestos. Salivary gland tumors are rare. Doctors know that salivary gland cancer occurs when some cells in the glands develop mutation in their DNA. This allows the cell to multiply and grow rapidly. Mutated cells continue multiplying while the other cells die. These cells accumulated form a tumor can invade the surrounding tissues and metastasize.
There exist different types of salivary gland tumors. They are classified based on the type of cells involved in the tumors. By identifying the type of salivary gland tumor, doctors can decide as to what treatment option is the best for you.
The most common benign (non cancerous) salivary gland tumor is Pleomorphic Adenoma. It is typically a slow growing tumor that mostly occurs in the parotid gland. Other benign salivary gland tumors are:
Types of malignant salivary gland tumors include:
The first sign may be a lump inside your mouth under the tongue or inside of your cheek. These lumps grows slowly and don’t hurt. There might be discomfort in swallowing the food, and the voice might become hoarse.
This type of cancer can spread along the nerves, so you might have some pain or numbness in the face. On facing any of such symptoms, visit your doctor immediately.
Signs and symptoms of a salivary gland tumor may include:
If your doctor thinks you might have adenoid cystic carcinoma, the first step most often is a biopsy. The doctor will take a small sample of the tumor, by making a small cut or with the help of a needle. This sample is sent to the laboratory to check under the microscope for any signs of cancer.
These kinds of tumors can take different forms and shapes like solid, round and hollow like tube, to cribriform, which means they have holes in them like Swiss cheese. The solid tumors happen to grow faster.
In order to find more about the size and location of a tumor, or to check if the cancer has spread, the doctor might suggest either of the following tests:
Certain factors that might increase the possibility of salivary gland tumor are as under:
Salivary Gland Cancer tumors are classified using a AJCC (American Joint Committee on Cancer) staging system taking into consideration the following:
Keeping size of the tumor in mind, a scale classifies the tumour as T1, T2, T3 up to T4 where T1 is designated for a tumour which is 2cm or less, while tumours greater than 6 cm in dimension are classified as T4.
Based on the combination of the three elements, a tumour is diagnosed as stage 1, 2, 3 or 4 with 4 being the most serious of all the stages. ACC diagnosis being very unpredictable can result into various outcomes irrespective of the stages. However, the larger the tumor size and occurrence of metastasis indicate that an aggressive treatment is required for the patient.
There is another staging system used by the pathologists which is based on tumor histology which is as under:
Surgery followed by radiation therapy is the most common treatment for ACC. In large number of cases these two standard treatments stop the cancer and avoid recurrence. After the tumor is removed by a surgery, it is sent to a lab for testing its margins. If the lab report indicates that the removed tumor has negative margin, it is good news which means the entire cancerous tumor has been removed in the surgery. If the lab test results indicate positive margin, it means; there might be residual cancerous cells yet left at the site of the surgery.
Radiaton therapy for the residual cells is the most common treatment type adopted Onco-surgeons. Some doctors even follow-up with radiation therapy for tumors with clean margins due to the tendency of ACC having invisible microscopic spread.
Certain tumors cannot be surgically removed due to their location and proximity to critical organs. In such cases radiation treatment is the only option and recommended choice for treating these tumors.
For both primary and metastatic tumors, the treatment choices and decisions can be complex and varied as details like tumor size, location of the tumor, adjoining critical organs, infiltration, available treatment centres, finance and insurance resources, physician recommendation and comfort of the patient have to be taken into consideration.
Variety of chemo and targeted drug treatments are available as standalone or as a part of clinical trials. However, ACC patients like other cancer patients have pursued many Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) as part of their recovery plan, with various degrees of positive benefits.
A remission state is when the cancer cannot be detected in the body any longer and there are no symptoms of the disease left. This is called NED or “no evidence of disease”. A remission can either be temporary or permanent. The feat that cancer might reoccur haunts a lot of patients. It is important that you talk with your doctor about the possibility of reoccurrence of cancer; and the means to deal with it. This will help you to keep prepared, if the cancer strikes again, by chance.
Recurrent cancer can occur at the original site of cancer; this is called local recurrence, or it may occur somewhere nearby the original site, which is called regional occurrence. If the recurrent cancer happens at some other site, it is called distance recurrence.
Even if the tumor is extracted with clean margins, ACC has high trend to recur and metastasise to other parts of the body even after some years. This long term recurrence and metastasising are major causes of deaths in ACC rather than initial failure to treat the tumor. Metastasis occurs when cancer cells move to other parts of the body through the blood stream, as a result tumors show up in other parts of the body. These tumors are called “mets”. The most common site of ACC tumor metastasising is lungs, the liver and then the bone.
If the ACC metastasises, your treatment plan might include a combination comprising surgery and radiation therapy. Doctors might also advise palliative care for relieving symptoms and side effects.
Diagnosis of metastatic cancer can be a shock to patients and difficult to bear. Patients and family members are encouraged to discuss their problems and share their views as to how they feel with the health care team of doctors, nurses and others. It also might be a good idea to become part of the support group which can help reduce the stress and keep the patient motivated during the treatment process.
Side Effects from Treatments
The side effects of treatment as experienced by ACC patients are both long term and short term. Surgery and radiation to the head and neck region can give rise to a number of issues due to removal and treatment of the tissue in oral cavity and other adjoining areas. This can result into chronic pain, dental issues and aberrations in the facial structure that directly affects the appearance of an individual.
Radiation therapy: common side effects
Second level of side-effects occurs due to palliative treatments. E.g. brain swelling that causes nausea, due to radiation treatment targeted to neck and head is treated by high dose steroids. However, long term side effects of steroid usage results into damage of connective tissues and premature cataracts.
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma is a slowly progressing but a dangerous cancer type that rise from the salivary glands. Timely treatment can help save your life and improve the quality of life. Timely treatment, post treatment follow-ups to trace any recurrence of the cancer is very important, as ACC metastasises easily to sites like lungs, liver and the bones.
Shalby Hospitals’ Cancer & Research Institute at Ahmedabad and other centres in the country are well manned and equipped with the latest equipment for diagnosis and treatment of all cancer types. Our team of expert oncologists, onco-surgeons, radiologists and other cancer specialists diagnose and design a treatment plan; keeping in mind your overall health and progression of the cancer.
In our modern lives, the adage “Sitting is the New Smoking” has become increasingly relevant. But beyond this familiar warning lies a more alarming truth: our daily choices significantly impact our health. The combination of prolonged inactivity, indulgence in junk food, smoking,...
India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, with a population of over 1.3 billion people. However, this economic and demographic growth also brings many challenges for the healthcare system, especially in terms of managing the burden of non-communicable diseases...
Just like the women were oppressed for centuries together, the story of men is no exception. While women have been the primary victims of gender-based oppression, men have also been subjected to unfair and unrealistic expectations that have caused them physical and...