The Thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of your neck; it is wrapped around the windpipe (trachea). There are two thyroid lobes on either side of the neck, joined by a thin tissue area in the middle of the gland – called isthmus.
The thyroid makes use of iodine for producing various hormones. The main hormone produced by the thyroid is the Thyroxine, also known as T4. Thyroxine is delivered to your body tissues through blood and once it gets delivered, a very small amount gets converted into triiodothyronine (T3). This happens to be the most active hormone.
The gland carries some of the most vital functions like regulating various metabolic processes in your body. Thyroid gland’s functioning is controlled by a feedback system that involves your brain. If the thyroid hormone level goes low, the hypothalamus present in your brain will produce the thyrotropin hormone which will make the pituitary gland – present at the base of your brain, to release the thyroid stimulating hormone. It will stimulate your thyroid gland to produce more of Thyroxine.
Any disorder that hampers the functioning of thyroid gland leads to thyroid disorders. As thyroid gland is being managed by the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland, any problem that affects these tissues can hamper the thyroid functioning, leading to various thyroid problems.
Hypothyroidism is a condition that occurs when the thyroid gland produces an inadequate amount of the thyroid hormone. Hypothyroidism can also develop from the various problems that happen in the thyroid gland, hypothalamus or the pituitary gland. The signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism include:
If the thyroid hormone is produced in an excess amount, it leads to a condition known as Hyperthyroidism.
As compared to hypothyroidism, it is a lesser common condition. Hyperthyroidism increases your metabolism and the symptoms associated with the condition include:
It is also a common disorder associated with thyroid gland, characterized by augmentation of the thyroid gland. Goiter is often associated with the different thyroid problems as hypothyroidism, or hyperthyroidism.
The primary cause of goiter is said to be the lack of iodine in the daily diet. Treatment of goiter depends on its size, the symptoms as well as the underlying cause. If the goiter is very small, isn’t causing any problem and is hardly noticeable; no treatment would be needed. Often goiter doesn’t cause any symptom, but if the condition is a bit severe, the prominent symptoms would include:
Nodules are the lumps or abnormal masses present in the thyroid that are caused by mild cysts or tumors. In some rare cases, the nodules can also be caused due to cancer of the thyroid. These nodules can be single or multiple and the size can diversify.
When the nodules become very large, they tend to cause symptoms as the nearby structures get compressed. Some of the symptoms include:
The precise cause of thyroid nodules is not known. It is mostly seen that nodules have a family history, which makes it clear that they have a genetic base. Nodules are even found in people who are iodine deficient.
Thyroid cancer is more common in women as compared to men. Based on the thyroid cell type that has become cancerous, thyroid cancer has been divided into different types. When diagnosed at an early stage, thyroid cancer can be treated easily and the survival rate also stands high.
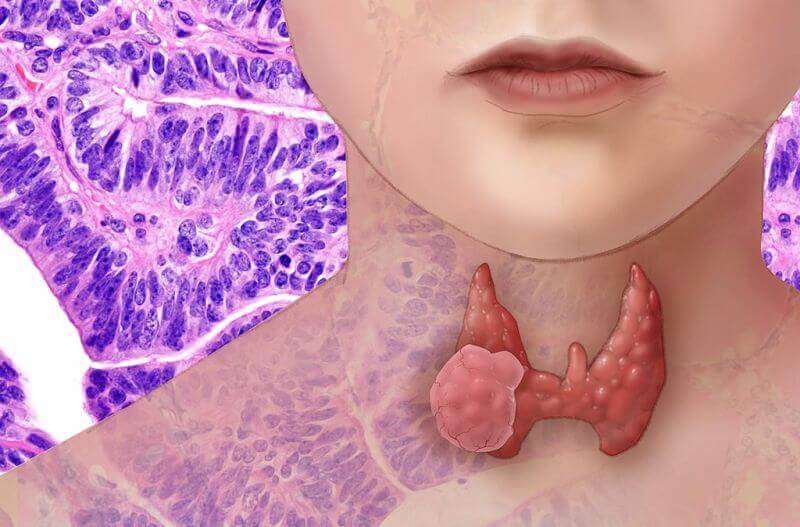
A thyroid cancer is likely to cause any of the following symptoms:
The precise cause of thyroid cancer is not known as of yet. However, there are various factors that increase your risk of developing thyroid cancer. But in many cases, people develop thyroid cancer without being subjected to the risk factors.
There are many factors that are known to increase your risk of developing any of the thyroid problems. Some of these common risk factors include:
Gender: Most of the thyroid disorders are common in women as compared to men. This is why experts consider that women are at a higher risk of developing thyroid disorders.
Age: People who are 50 years old or above also stand at a higher risk of suffering from a thyroid disorder. And it is common for both men and women.
The family history of thyroid disease: If your family had a personal history of thyroid diseases, there are higher chances for you to develop a thyroid disorder.
Thyroid surgery: If all or some part of your thyroid is removed surgically, it can increase a risk of hypothyroidism, which denotes an underactive thyroid.
Radioactive Iodine Treatment (RAI): This is used in treating Graves’ disease or hyperthyroidism. It is even used as a part of thyroid cancer treatment surgery, which results in hypothyroidism.
Cigarette Smoking: It subjects you to autoimmune thyroid disease. Cigarettes have a chemical known as thiocyanate, which can adversely affect your thyroid gland while acting as an antithyroid agent. Studies have also revealed that smoking also increases
the risk, side effects and severity of hypothyroidism if you have Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Smoking also worsens the repercussions of thyroid eye disease, which is a Grave’s disease complication. Smoking even cuts down the potency of thyroid eye disease treatment.
Goitrogenic Foods: Certain foods, which if eaten raw and in excess can enlarge the thyroid resulting in goiter because they naturally contain goiter promoting chemicals (goitrogens). Foods that are high in goitrogens include:
Iodine Exposure/Intake: Often people, who are iodine sufficient, tend to take iodine or herbal supplements containing iodine, either in the pill or liquid form. However, it can increase the risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease as well as hypothyroidism. Sometimes, it can even lead to hyperthyroidism or thyrotoxicosis.
Iodine Deficiency: As stated earlier, iodine deficiency can lead to hypothyroidism and goiter. It is most commonly seen in the people from the U.S. as their salt intake is very less. Iodine deficiency is also common in the people living in mountainous or inland areas.
Medications and Treatments: Some medical treatments and drugs like Interferon Beta-1b, immunosuppressants, Interleukin-4, antiretrovirals, bone marrow transplant, Lithium, monoclonal antibody (Campath-1H), and amiodarone (Cordarone), are known to increase the risk of an underactive thyroid.
Medical Radiation Exposure: If your neck area gets exposed to radiation, whether during medical treatments for neck or head cancer, it can increase your risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease and thyroid cancer.
Environmental Radiation Exposure: If you encounter an accidental radiation exposure occurring in the environment, you can be at risk of developing autoimmune thyroid disease and thyroid cancer.
Thyroid disorders can affect anyone; however, taking care of certain things can help in preventing the condition. And if you already have the thyroid disorder, you can always make efforts to manage it so as to prevent any further complications.
Let us have a look at some of the methods that can help you in preventing thyroid disorders:
Quit Smoking: Smoking can increase the risk of developing thyroid in both women and men alike. This is because cigarettes contain toxic chemicals and substances like thiocyanate which subject you to developing thyroid disorders. It can even interfere with your thyroid treatment. This is why it is advised that you quit smoking so that the treatment can be planned effectively and the results stand satisfactory.
Treat the Antibodies: Antibodies are known to trigger the signal of the nonessential quantity of the thyroid hormone. Thyroid receptors in your body also get blocked due to the poor signal of the antibodies. If the antibodies are not treated, the thyroid problem can get complicated and even medicines for thyroid treatment won’t have the right effect.
Avoid Soy Products: Most people love soy products, found in different forms like powders, tofu, creams, sauce and various other food products. Intake of soybean to an extent is definitely healthy, but going overboard with it can lead to various disorders and subject you to thyroid problems. It should be taken care that you consume soybean more in its natural form rather than going for the processed version.
Along with these, you should also make it a point to maintain a healthy lifestyle and eat a healthy diet. Exercise should be made a part of your daily routine and regular check-ups must be followed without fail.
While managing thyroid, along with proper medication, it is very important that you take good care of what you eat. Your diet has a very crucial impact on your thyroid. Below mentioned are some of the best and worst foods for your thyroid.
Salt: Thyroid needs iodine to function well. You must ensure that you eat iodine rich foods as fish and dairy products. Moreover, the table salt you use must be iodized.
Leafy Greens: Leafy green vegetables like spinach, lettuce and others are rich in magnesium; which is a vital mineral that plays a huge role in body processes. If you experience muscle cramps, fatigue or note changes in your heartbeat, it is indicative that you are not getting enough amount of leafy greens. And they even contribute to keeping your thyroid healthy.
Nuts: Different nuts as almonds, cashews and pumpkin seeds are rich in iron and help your thyroid is functioning well. Brazil nuts are an excellent choice for thyroid because they’re not only rich in iron but are even good source of selenium, which is also a mineral type that supports the thyroid.
Seafood: A variety of seafood as shrimp, fish and seaweed make for great sources of iodine. Though iodine is good for thyroid, an excess of iodine can be very harmful. Avoid foods like kelp which are very high in iodine content.
Kale: It happens to be a mild goitrogen and is also known to prevent the thyroid from getting the needed amount of iodine. If your iodine intake is very less, eating kale in abundance will not really be a problem. However, if you are getting the needed amount of iodine from your diet, then you should restrict the intake of kale. It applies to Brussels sprouts, cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower.
Soy: In some cases, certain chemical as found in soy products such as soy milk or sauce is known to limit thyroid from producing hormones. But this only happens when you are not getting enough amount of iodine and you consume soy products in a very large quantity.
Organ Meats: Eating kidneys, liver or heart as part of your meat diet can subject you to consume more of lipoic acid. It is a type of fatty acid found in organ meats and some other food types. It is even available as a supplement but too much of lipoic acid is a matter of concern as it can affect your thyroid’s working. Moreover, lipoic acid can even affect the thyroid medicines you take.
Gluten: It is a protein type that’s found in barley, wheat and rye. If you have been diagnosed with celiac disease – an autoimmune disease where gluten ingestion damages the small intestine – gluten can be harmful to thyroid. People with celiac disease also have other autoimmune disorders like Hashimoto’s disease (underactive thyroid) and Graves’ disease (overactive thyroid). You should opt for a gluten-free diet to prevent the thyroid disease.
Neglecting thyroid problem can subject you to various complications. If the thyroid is not treated timely and properly, you can suffer from complex health conditions that can sometimes even prove to be fatal.
If you have hyperthyroidism, which is an overactive thyroid, delayed treatment can subject you to the following problems:
In case of hypothyroidism, where you have an underactive thyroid, the complications can include the following:
As stated earlier, treating thyroid disorder on time can help prevent various complications. And for effective treatment, diagnosis is the first key. Thyroid disorder diagnosis can involve various methods, your doctor will choose any one or a combination of methods to diagnose thyroid.
Here are some of the ways used to diagnose thyroid disorder:
If your doctor suspects that you have the thyroid, he or she will recommend a blood test to confirm the same. It is one of the commonly suggested diagnostic ways for thyroid.
If your thyroid has enlarged or has been potentially atrophied, and if nodules have been detected or suspected, you will be suggested to undergo different imaging tests that can help in the proper diagnosis of your thyroid condition.
A needle biopsy, which is also known by Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) biopsy, helps evaluate the sceptical thyroid lumps and nodules. In this process, a thin needle will be injected directly into your nodule. Then some cells will be withdrawn and they will be evaluated for cancer.
There are various ways of treating thyroid but that depends on your thyroid condition, intensity and your overall health.
Some of the thyroid disorders can easily be treated by medications while a few cases where medications don’t work fine, then surgery is the best option.
In case of hypothyroidism, medication is mostly given for replacing the missing thyroid hormone. A synthetic thyroid hormone is given in the pill form, orally. For treating hyperthyroidism, medications work by reducing the production of thyroid hormone or by preventing the release of the thyroid hormone from the gland. Some medicine types can even aid in regulating the symptoms of hyperthyroidism, for instance, an increased heart rate. If medication doesn’t help in controlling hyperthyroidism then radioactive ablation is the right choice. This process calls for iodine doses labeled with radioactivity which carefully destroys the thyroid tissue.
Surgery is recommended in the cases where a large Goiter needs to be removed or there is a hyperfunctioning nodule present in the gland. Surgery is even required if there is a likelihood of thyroid cancer. In the cases where the thyroid gland is completely removed, individuals will have to opt for synthetic thyroid hormone throughout their life. Thyroid surgery is even used in treating Graves ‘disease (subtotal thyroidectomy).
As one of the prime endocrine gland, the thyroid gland produces two vital hormones; hormones triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) which regulate the metabolic functions and protein synthesis in your body.
For the proper functioning of all body processes, it is important that the thyroid gland continues to work efficiently. Any disorder related to thyroid must be diagnosed and treated timely so as to prevent complications.
As one of the leading hospitals in India, Shalby Hospitals, Ahmedabad has a dedicated endocrinology unit, headed by highly efficient and trained Endocrinologist. Our team brings to you the most effective medical care for thyroid regulation and management. They specialize in offering customized treatment approach for various thyroid disorders. From diagnosis to treatment and management of thyroid disorders, our experts are always ready to help you with the best viable options.
Right from finding the best school to providing the latest gadgets, designer clothes and dishing out nutritious recipes, parents leave no stone unturned to give their children the best of everything. The new-age parents invest a lot of their time, effort and...
Diabetes is a condition when your blood sugar level or glucose tends to fluctuate all of a sudden— too much content of blood sugar results in diabetes. Types of diabetes are differentiated according to their symptoms and consequences. It is essential to...
Like the Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes is also a diabetes type which usually occurs at the time of pregnancy. It increases the blood sugar levels when you are pregnant. However, it is not a condition to worry about...